Pd-catalyzed deuteration of aryl halides with deuterium oxide
Yu Chen1,#, Ruyi Yuan1,#, Tongtong Zheng1, Qingting Guo1, Yingming Yao1 (姚英明)*, Li Zhang1 (张力)*
1Key Laboratory of Organic Synthesis of Jiangsu Province, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, P. R. China.
Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2584
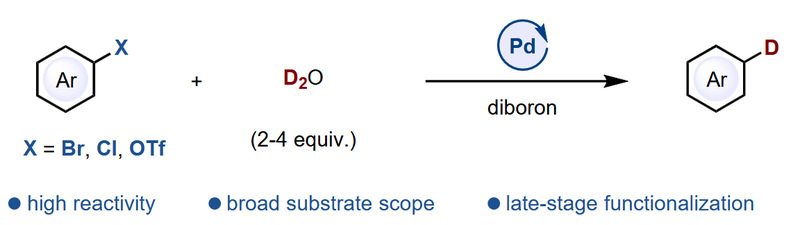
Abstract: Late-stage deuteration of aryl halides with deuterium oxide is a highly desirable but challenging transformation, primarily due to the difficulty of activating inert carbon-halogen bonds and the umpolung of deuterium oxide in the presence of various functional groups. To achieve this transformation, efforts have been made to develop photo-chemical, electro-chemical, or mechano-chemical strategies. However, these approaches often require specialized setups or activated substrates. Despite the well-known functional group tolerance of palladium catalysis, which makes it valuable in late-stage functionalization, a palladium-catalyzed deuteration of aryl halides with deuterium oxide has remained elusive. Herein, a deuteration reaction of aryl bromides, chlorides, and triflates with deuterium oxide has been developed, through palladium catalysis. Chemical equivalent amount of D2O is required for inert substrates like aryl chlorides. The reaction features high functional group tolerance, making it suitable for late-stage deuteration.
Article information: //www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-57855-x